
/GettyImages-607489868-685e70c38e04403489137eb63dc8b12a.jpg)
( Hamner, 1994 Hamner, 1995 Hartwick, 1991 Seymour and Sutherland, 2001 Tibballs, 2006) Once the polyp has finished budding, it develops into a juvenile medusa, which grows into a sexually mature medusa. Once fertilization occurs, planula attach to a hard surface and develop into a small polyp, which may asexually reproduce via budding. Mature box jellyfish release sperm or eggs into the water.

( Hamner, 1994 Seymour, et al., 2004)Įvery spring, box jellyfish gather to spawn in rivers and similar bodies of water. Shortly after spawning, box jellyfish die. Here, jellyfish release their sperm and eggs directly into the water. ( Hamner, 1994 Hamner, 1995 Hartwick, 1991 Seymour and Sutherland, 2001)īox jellyfish find mates by swimming to freshwater rivers during the spring.
A BOX JELLYFISH FULL SIZE
Once in the sea, a maturing box jellyfish continues to grow until it reaches its full size of 16 to 24 cm. After a polyp has metamorphosed into a small medusa, it travels from freshwater rivers to the sea. A polyp can reproduce asexually via budding. Polyps rely on schools of plankton for food. Polyps usually attach themselves to a surface where they are not exposed, often on the underside or a crevice of the hard surface. Polyps use their two tentacles to attach to a hard surface, such as a stone or the shell of other animals. Planulae soon develop into polyps, which are sessile and small (1 to 2 mm) and look like a living ball with two tentacles. ( Carrette, et al., 2002 Currie and Jacups, 2005 Hamner, 1995 Seymour, et al., 2004 Tibballs, 2006)Īfter the reproduction of sexually mature medusa, box jellyfish develop planulae, cells grouped together after fertilization. Box jellyfish contain sensory organs including 24 eyes, but they do not have a brain. Each tentacle contains millions of nematocysts, which are microscopic hooks where venom is held and delivered. Each of the tentacles has a slight blue-gray tint and can grow up 3 m in length. There can be as many as 15 tentacles hanging from each of the four pedalia for a total of up to 60 tentacles per jellyfish. The tentacles of box jellyfish dangle from pedalia, the corners of the bell. The bell is transparent and is usually between 16 and 24 cm, though some reach a diameter of 35 cm. The name box jellyfish is derived from the shape of their bell, which is box-shaped when healthy. ( Currie and Jacups, 2005 Hamner, 1995 Tibballs, 2006) Once young jellyfish mature into medusa, they follow the river out to sea. Box jellyfish also inhabit shallow rivers during the reproductive season and during their polyp stage. During heavy storms, they move into deeper waters where the water is calm to avoid damage.
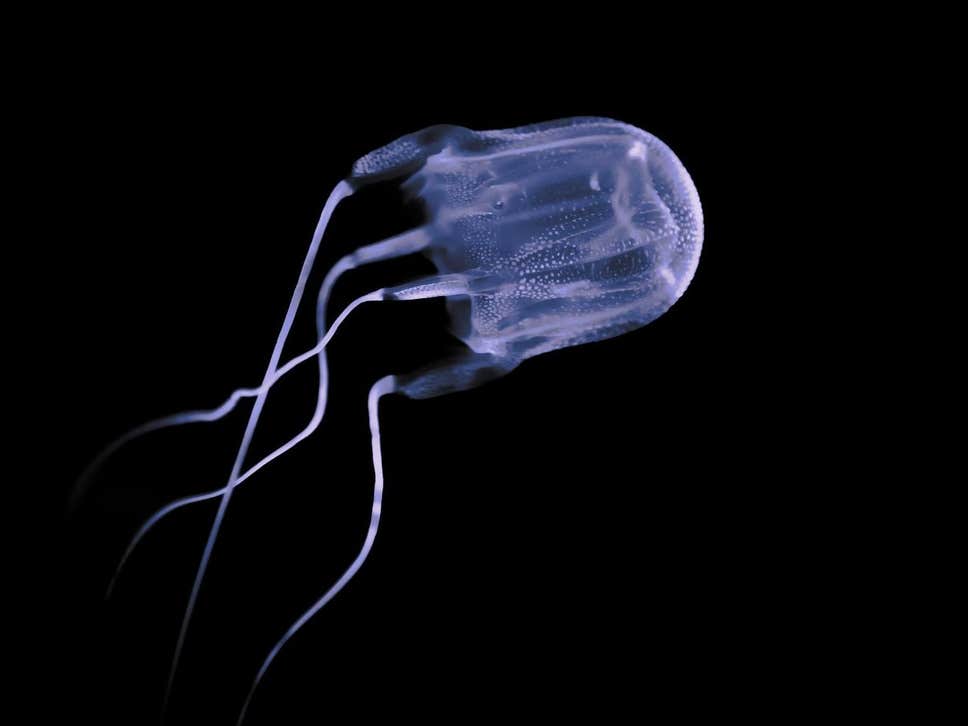
They are mainly found in the ocean but are also found inland in freshwater rivers and mangrove channels when spawning. ( Hamner, 1994 Hamner, 1995 Tibballs, 2006)īox jellyfish tend to inhabit shallow, murky saline waters near Australia.

Box jellyfish may also be responsible for stings near the Philippines. Humans are frequently stung by this species in the oceanic waters of Queensland, on Australia's eastern coast. Box jellyfish have been found in the waters on the western coast of Australia in the Exmouth Gulf to Gladstone in the northern waters of Australia. They inhabit parts of the Indian Ocean, Pacific Ocean, and the Great Barrier Reef. Chironex fleckeri, also known as box jellyfish, lives in and around the waters of Australia and Southeast Asia.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
